Building a text adjacency graph from product reviews with the Best Buy API
William Lyon
January 7, 2016
2 min read
This week I'm preparing a presentation for DataDay Texas about Natural Language Processing with graph databases and Neo4j. While doing some research I came across a great quote from Matt Biddulph:
“Nearly all text processing starts by transforming text into vectors” - Matt Biddulph
He is referring of course to building a vector space model from a text corpus as the first step of text processing. In the context of NLP with graph databases, the first step is building a graph model from the text corpus. In many cases this is a simple word adjacency graph.
Another resource I stumbled across on the internet this week is the Best Buy API. This is a great resource for playing around with text processing. Specifically, the Reviews endpoint provides access to a rich series of user generated text that we can use for text processing. I'm specifically interested in text summarization and opinion mining so this is a perfect data set.

After registering with the Best Buy API and retrieving an API token this simple Python script can be used to fetch the first 500 product reviews for any Best Buy product and insert into Neo4j following the model of a word adjacency graph. Just replace the API_KEY and SKU variables to retrieve product reviews for any product.
from py2neo import Graph
import json
import requests
API_KEY = "YOUR_API_KEY_HERE"
SKU = "9439005" # Kindle Paperwhite
REQUEST_URL = "https://api.bestbuy.com/v1/reviews(sku={sku})?apiKey={API_KEY}&show=comment,id,rating,reviewer.name,sku,submissionTime,title&pageSize=100&page={page}&sort=comment.asc&format=json"
INSERT_QUERY = '''
WITH split(tolower({comment}), " ") AS text
UNWIND range(0,size(text)-2) AS i
MERGE (w1:Word {name: text[i]})
MERGE (w2:Word {name: text[i+1]})
CREATE UNIQUE (w1)-[:NEXT]->(w2)
'''
graph = Graph()
for i in range(1,6): # fetch first 500 reviews (5 pages at 100 per page)
r = requests.get(REQUEST_URL.format(sku=SKU, API_KEY=API_KEY, page=str(i)))
data = r.json()
for comment in data["reviews"]:
graph.cypher.execute(INSERT_QUERY, parameters={'comment': comment["comment"]})
Once the script runs, a snippet of the graph looks like this:
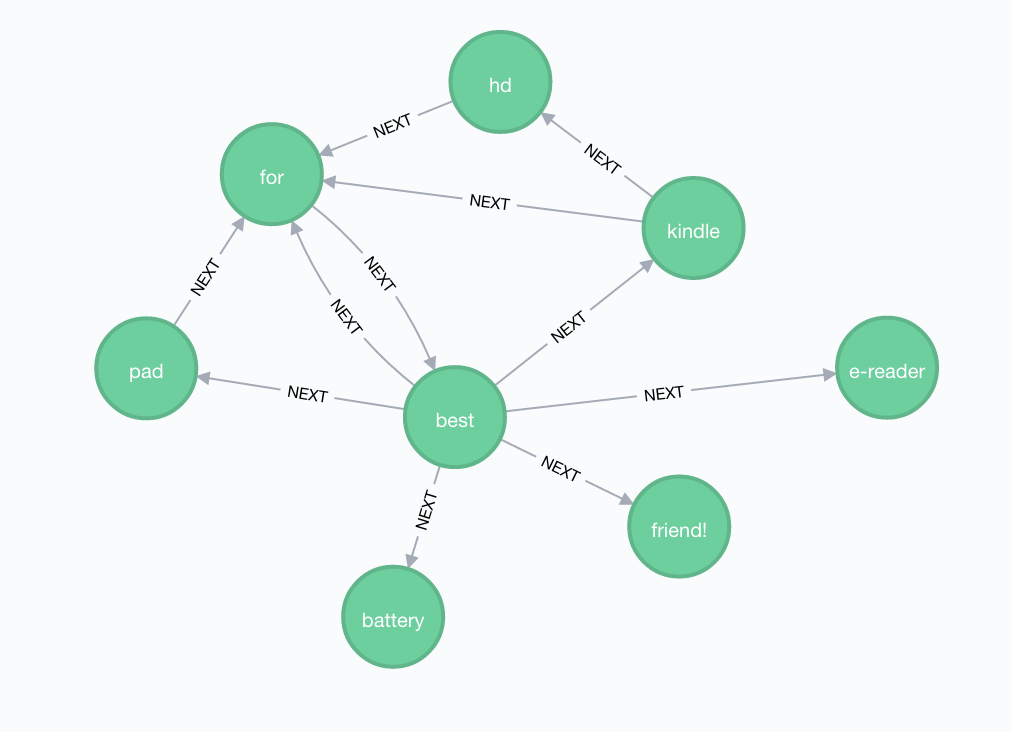
And now we can use Cypher to start analyzing our text corpus. For more reading on this area be sure to check out these great posts from Max and Michael.
Stay Updated
Get notified about new posts and videos